By quanyu lee
2025-01-07 01:25:10
Flexible Flat Cables FFC: Advancing Automotive Technology with Innovation
Flexible Flat Cables FFC in the Automotive Industry: Applications, Features, and Future Trends
With the rapid advancement of modern automotive technology, manufacturers continually explore innovative solutions to enhance vehicle performance, efficiency, and user experience. Against this backdrop, Flexible Flat Cables (FFC) have emerged as a vital component of automotive electrical systems, offering advantages such as flexible structures and compact size. This article delves into the current state of FFC applications in the automotive industry, their technical features, advantages, and future development trends.
Definition and Basic Concepts of Flexible Flat Cables (FFC)
Flexible Flat Cables (FFC) are ultra-thin, ribbon-like electrical connectors designed for streamlined signal and power transmission in compact electronic systems. Composed of multiple parallel conductive traces (usually copper) encased in flexible insulating polymer layers, FFC prioritizes space efficiency and adaptability. Their flat, lightweight structure enables easy routing in tight spaces, making them essential for modern devices like smartphones, laptops, and automotive electronics.
Key concepts include high-density interconnects, bendability for dynamic applications, and customizable configurations (length, pin count, and pitch). Unlike traditional round wires, FFC reduces clutter, enhances airflow, and improves reliability in high-flex environments while maintaining low electromagnetic interference (EMI). These features solidify FFC as critical components in miniaturized and high-performance electronics.
Applications of FFC in Automotive
Automotive Electronic Systems
Modern vehicles feature increasingly complex electronic systems. Unlike traditional round cables, FFC offers flexibility and customizability to meet intricate wiring requirements.
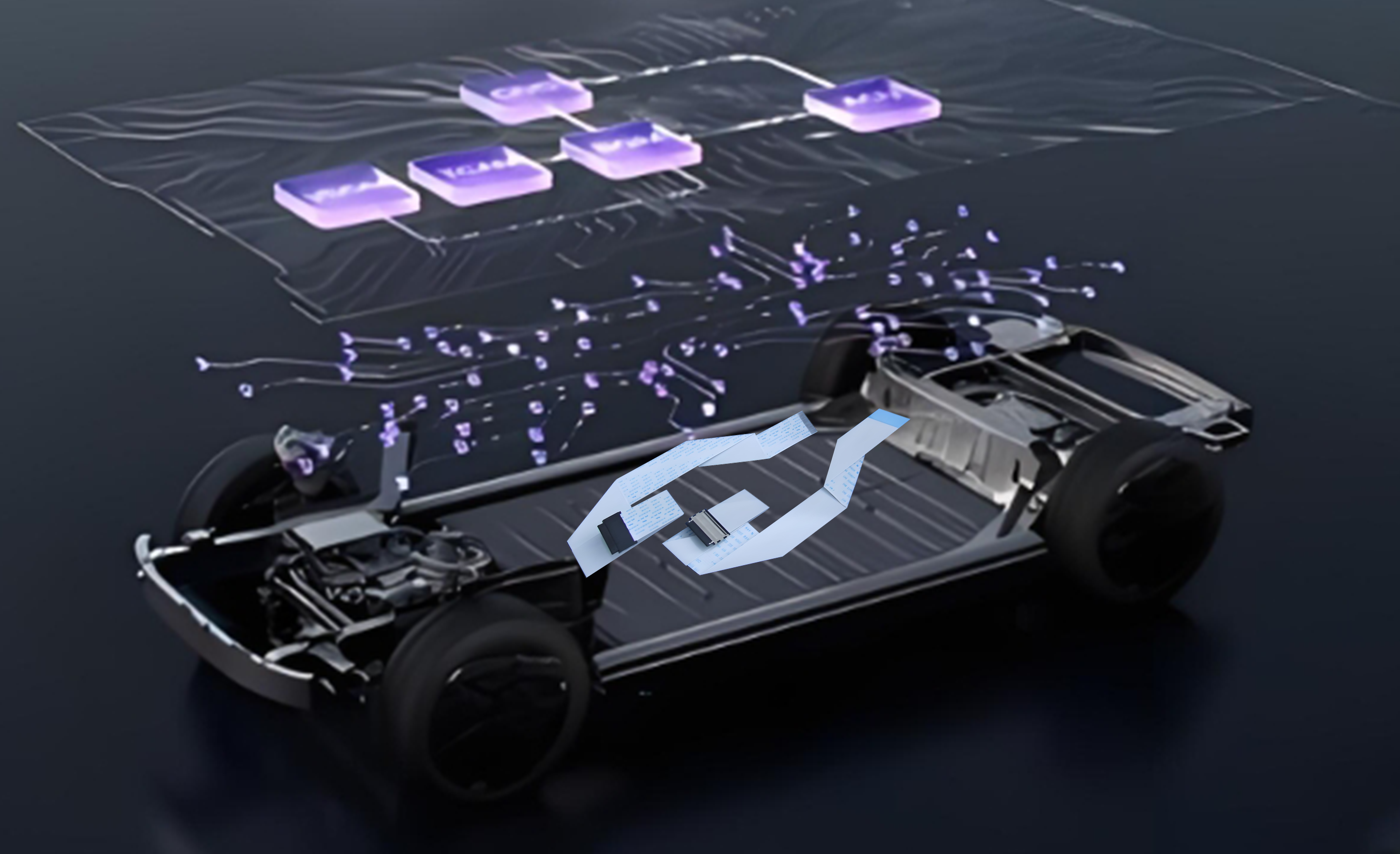

Powertrain Systems
With the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles, the complexity and electrification of powertrain systems have increased, making FFC more widely used.
Technical Advantages of FFC
-
High Flexibility
FFC's flexible structure allows for bending and twisting in confined spaces, accommodating intricate designs and improving overall performance. -
Lightweight Design
Traditional cables often require increased cross-sectional areas to maintain performance, adding weight. FFC combines lightweight construction with superior conductivity, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency or electric vehicle range. -
High Reliability
Materials like polyester film enhance FFC’s resistance to high temperatures and humidity, ensuring long-term stable operation even in harsh environments.
Future Trends of FFC
-
High-Speed Data Transmission
As automotive electronics demand faster data transmission, traditional cables face limitations at high frequencies. FFC’s low capacitance and inductance make it ideal for stable high-frequency transmission. -
Modular Design
Modular FFC designs simplify production and assembly while improving efficiency, consistency, and maintainability. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
With stricter environmental regulations, FFC will adopt more recyclable and eco-friendly materials, driving green innovation in the automotive industry.
Applications of FFC in Advanced Automotive Systems
Autonomous Driving Systems
- LiDAR: Ensures stable, high-speed connections between LiDAR and control units.
- Camera Systems: Supports real-time image transmission and power delivery.
- Electronic Control Units (ECUs): Enables efficient signal transmission and power distribution within ECUs.
Connected Vehicles (V2X)
- Communication Modules: Facilitates high-speed data transmission and stable connections for real-time information exchange.
- Display Systems: Enhances response speed and reliability in-vehicle display systems.
- ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems): Provides robust connections and data transmission for system stability.
Applications of FFC in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Battery Pack Connections: Ensures efficient energy transmission and signal stability between battery packs and Battery Management Systems (BMS).
- Motor Control Systems: Delivers signals and power for precise motor control and high-efficiency operation.
- Charging Systems: Enhances charging speed and reliability through efficient energy and signal transmission.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
- Power Battery Connections: Connect power batteries to BMS for optimized performance.
- Motor and Engine Control Systems: Facilitates coordination between electric motors and internal combustion engines.
- Energy Recovery Systems: Improves efficiency by transmitting energy and signals within recovery systems.
Conclusion
This article explored the applications of FFC in automotive electronics and powertrain systems, highlighting their advantages and future development trends. As automotive technology advances, FFC will play an increasingly prominent role. With the evolution of high-speed data transmission and modular designs, FFC is set to expand into new applications, driving innovation in the automotive industry.




