By quanyu lee
2025-01-08 08:27:17
New energy high voltage wiring harness introduction
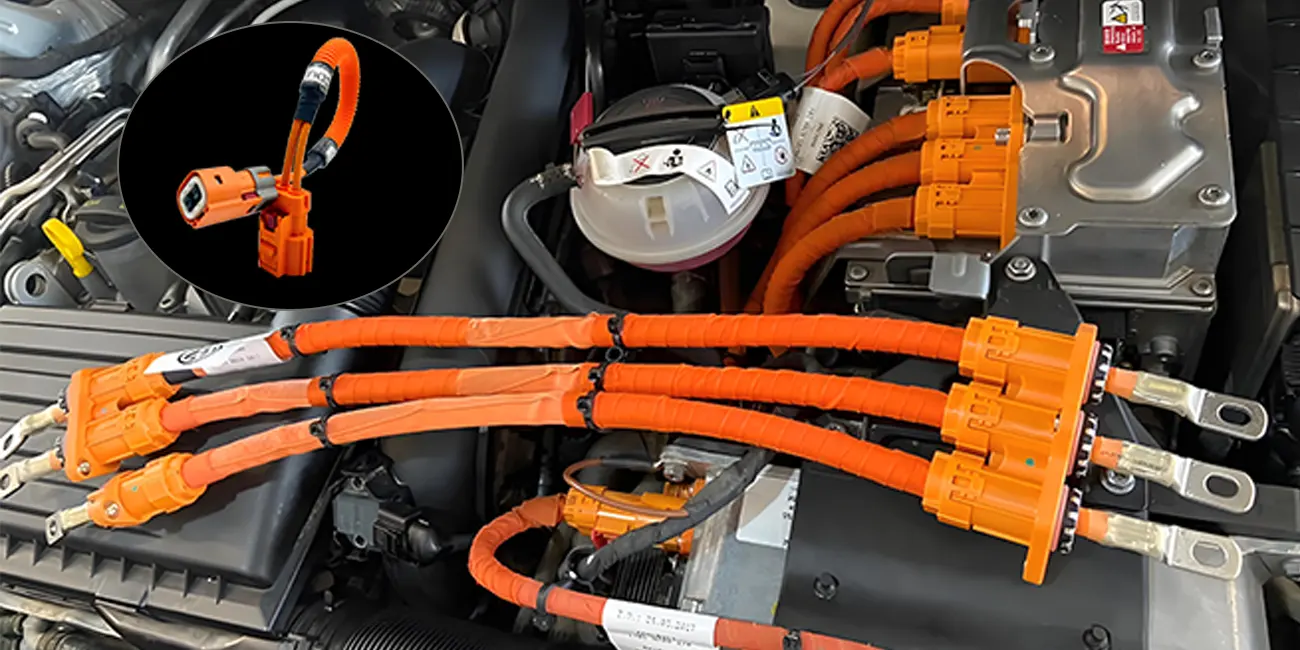
The high-voltage wiring harness of new energy vehicles is the core component of the vehicle's high-voltage power transmission. It undertakes the important task of connecting key components such as batteries, motors, and electronic controls. It must meet strict requirements such as high voltage, high current, strong electromagnetic shielding, and safety protection.

Its structure mainly consists of conductor (copper or aluminum), insulation layer (cross-linked polyethylene or fluoroplastic), shielding layer (tinned copper braided mesh), sheath (oil-resistant and corrosion-resistant material) and connector (with high-voltage interlocking, high waterproof grade and electromagnetic shielding functions).
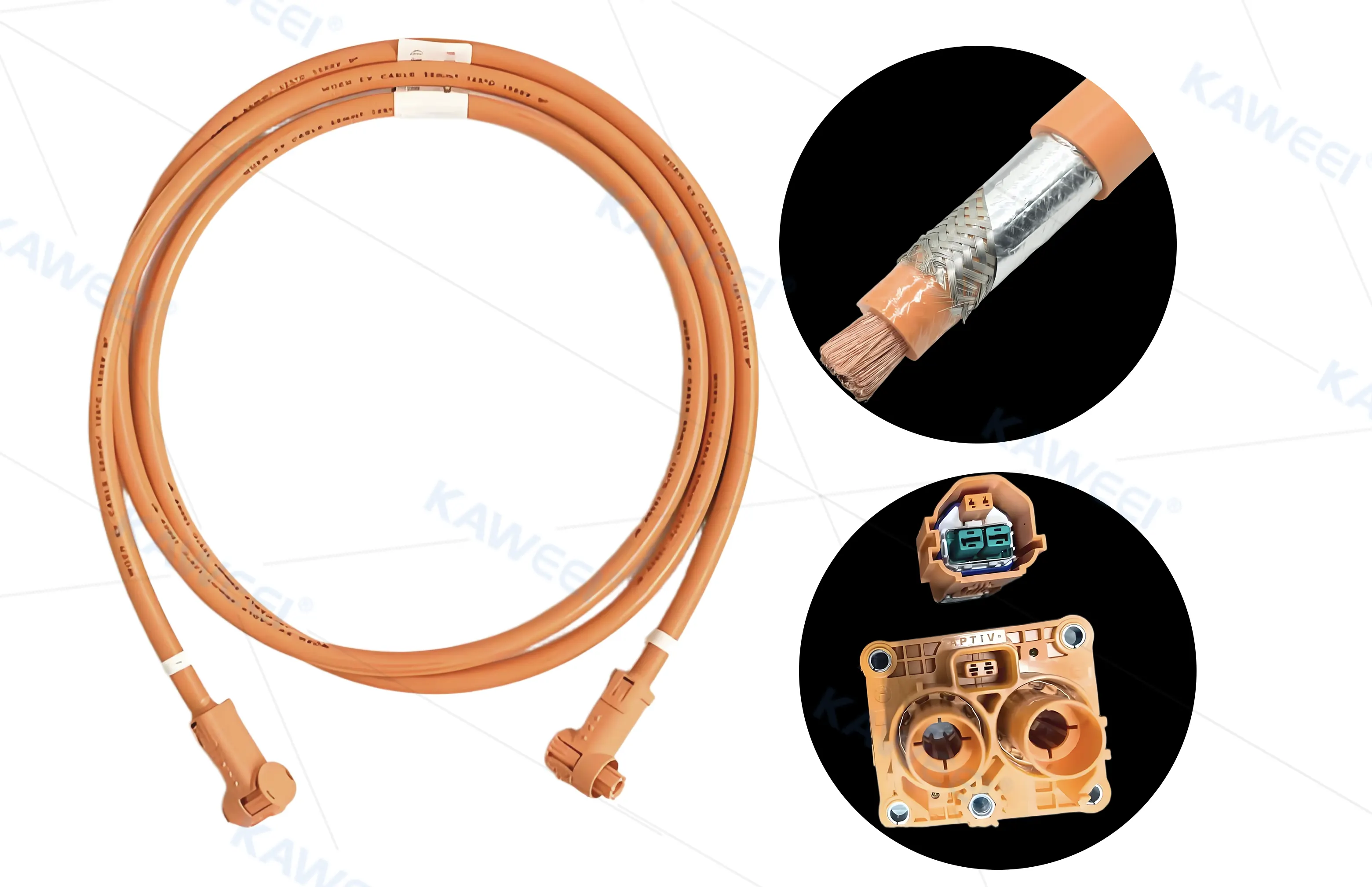

High-voltage wiring harnesses must meet safety requirements such as dual-track circuit design and orange warning signs, and pass strict insulation resistance (DC circuit > 100Ω/V, AC circuit > 500Ω/V) and withstand voltage tests (5000V/5 minutes without breakdown).

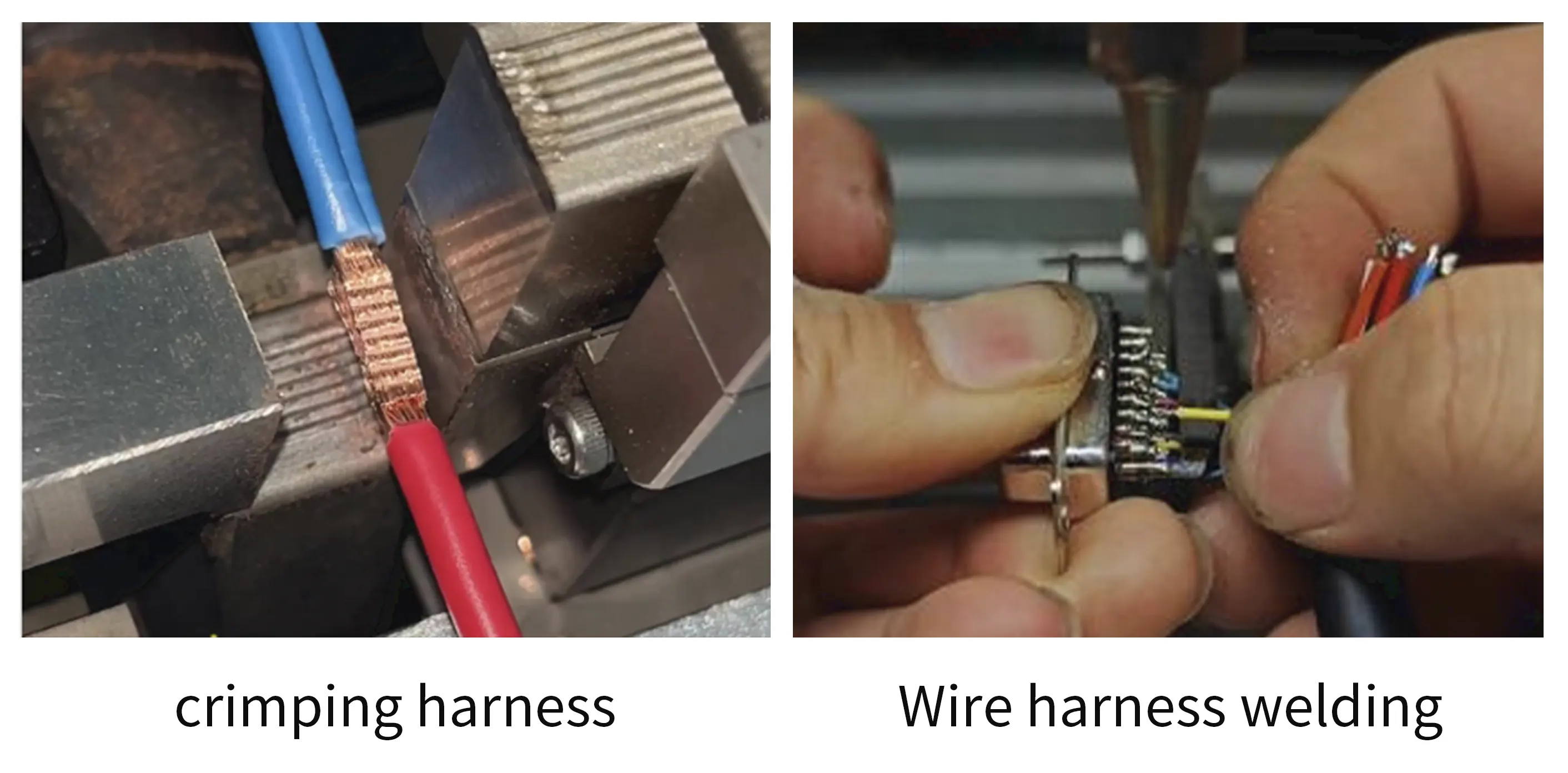
The main processes used are crimping and welding. The crimping process requires that the voltage drop at the crimping point is ≤15mV (16mm²/60A) and the minimum tensile force value meets the standard (such as 6mm² wire harness >600N).
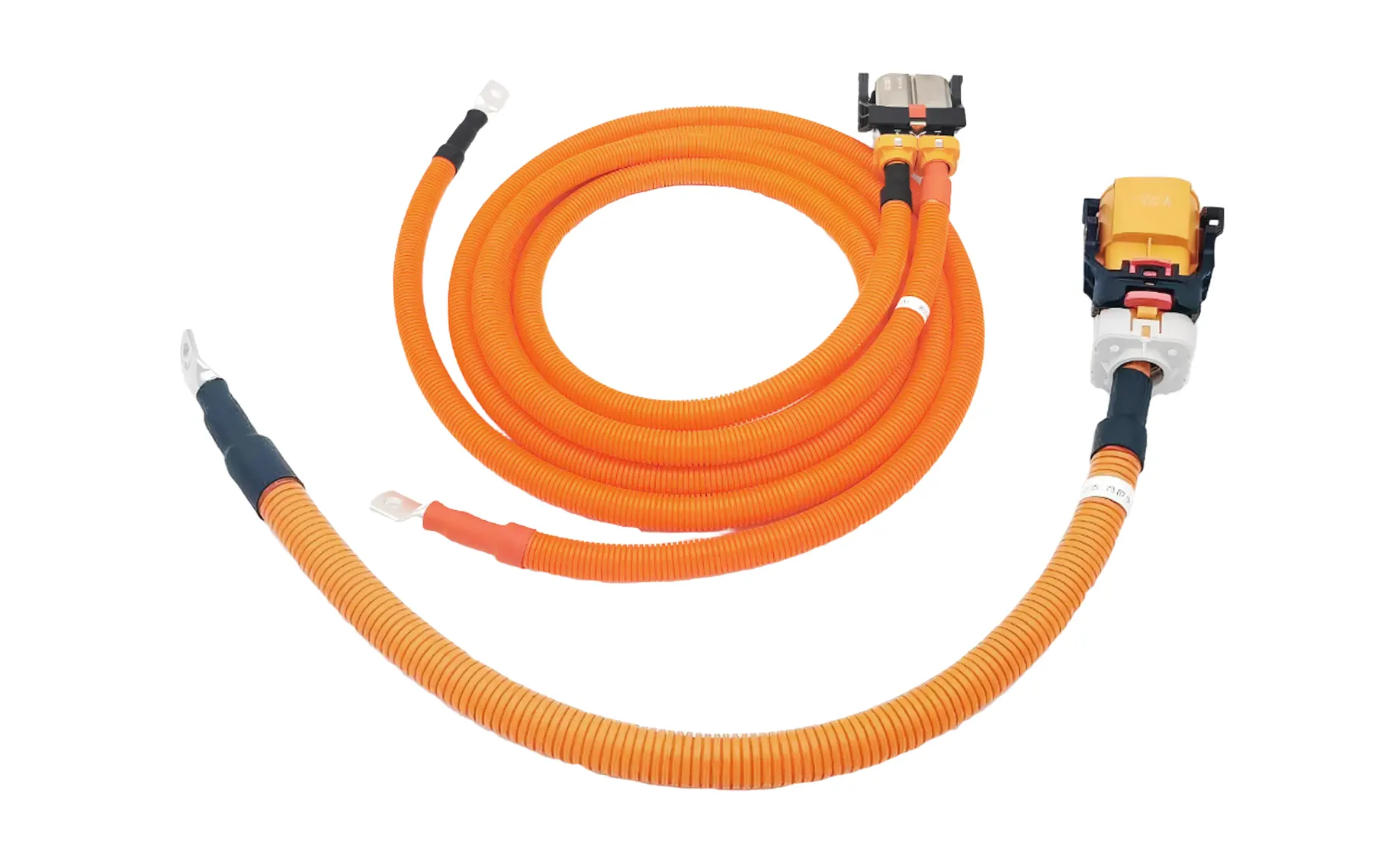
In terms of development trends, the application of aluminum conductors and composite shielding materials has expanded, and the integrated design of high-voltage wiring harnesses, PDUs, and controllers has improved space utilization and reliability. At the same time, industry standards such as QC/T 1037 and TCAS 356-2019 have been followed to enhance high temperature resistance and flame retardant properties.



