By quanyu lee
2025-04-02 07:07:36
Medical Wiring Harness Guide
Medical wiring harness is a specialized cable assembly used in medical equipment to connect electronic components or different parts. It is composed of multiple wires, optical fibers, connectors, and insulation materials combined according to specific specifications, and is responsible for functions such as power transmission, signal transmission, and data exchange. The following are its core features and applications:

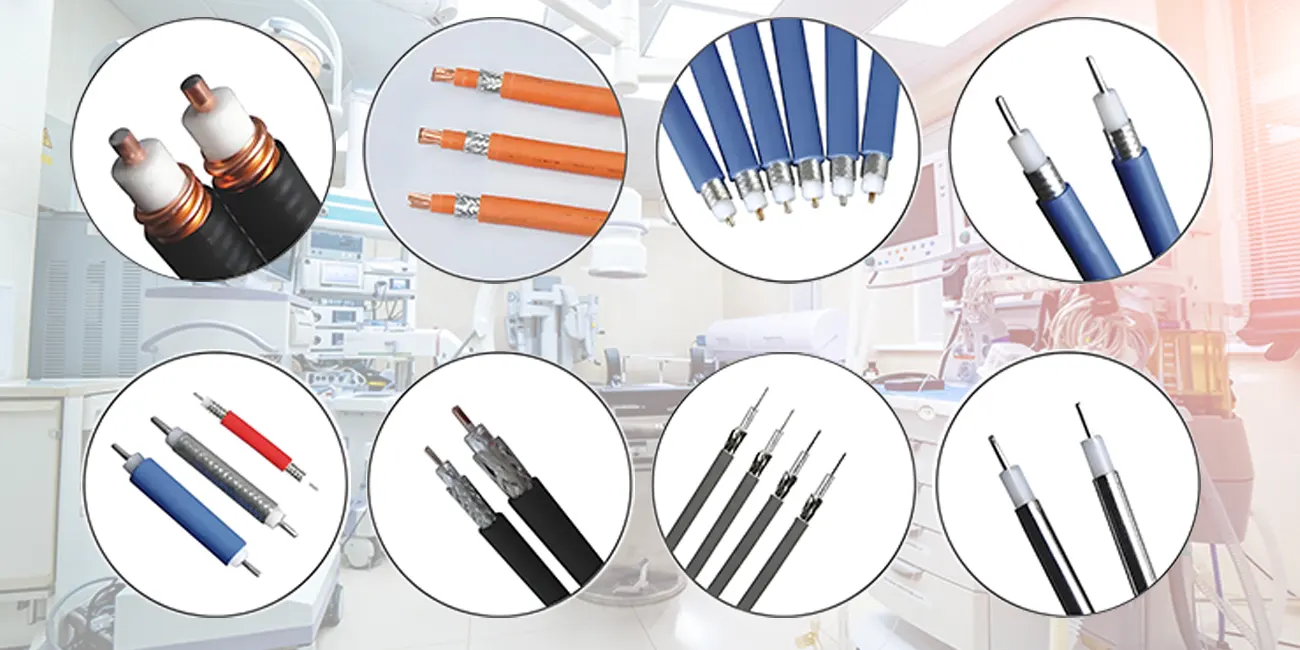
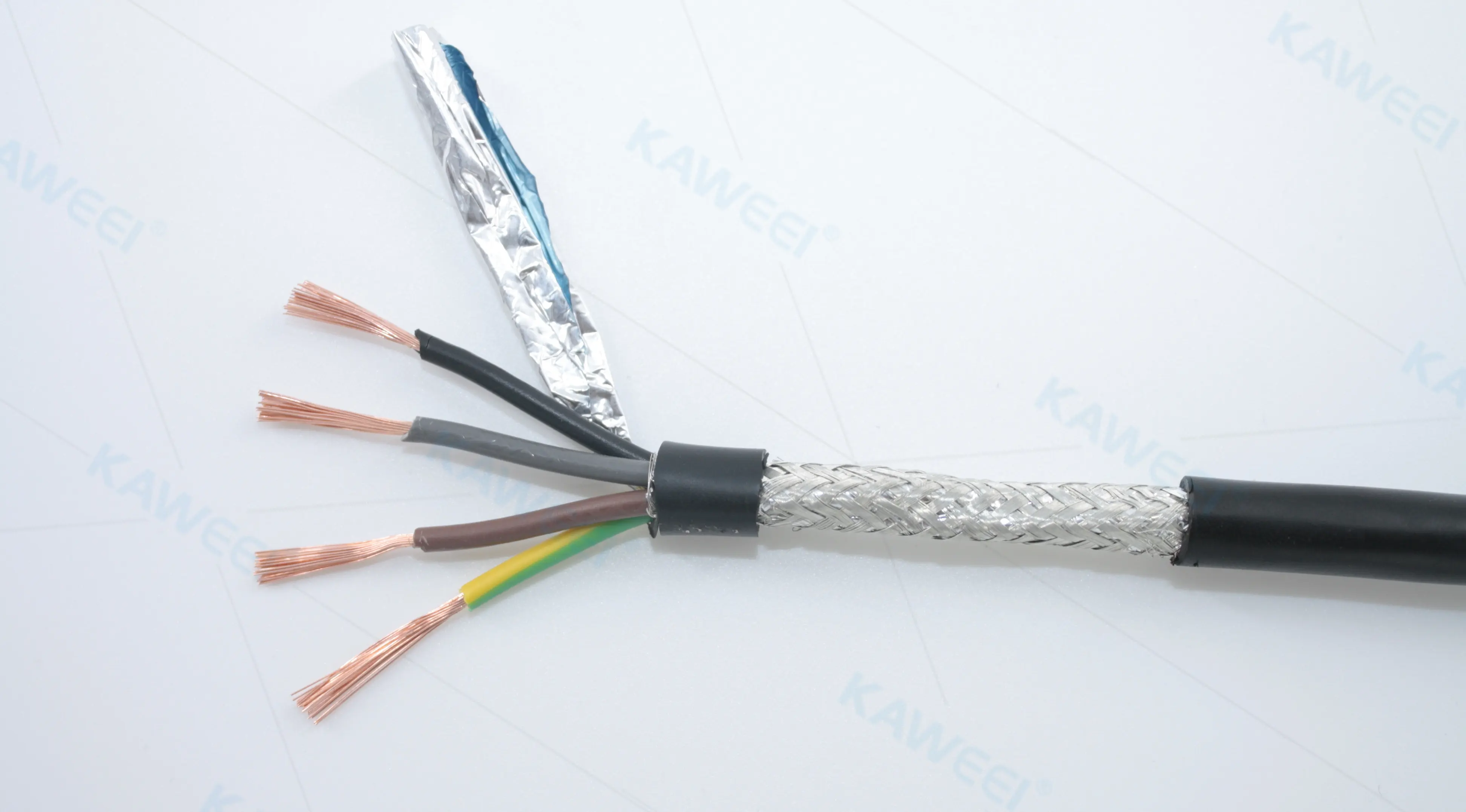
一、Composition and Structure
- Components such as wires, data cables, signal cables, optical fibers, and sensors are isolated and bundled with insulating materials to form a complete structure.
- Usually integrated connectors or plugs are used to meet the interface requirements of different medical devices.
二、Functional characteristics
- Power and signal transmission: Provide stable power supply for medical equipment and ensure efficient transmission of electrical signals and data.
- Safety requirements: It must comply with international standards (such as ISO certification) to avoid affecting equipment performance and patient safety due to signal interference or power abnormalities.

三、Materials for medical wiring harnesses
Conductive materials |
Insulation material |
High performance insulation and protective materials |
Biocompatibility standards |
| Copper: high conductivity, corrosion resistance, widely used in wire manufacturing, is the core conductive material of medical wire harnesses. | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): Low cost, resistant to chemical corrosion, commonly used as insulation layer for ordinary medical wire harnesses | Silicone: high temperature resistance (-60 ℃ to 200 ℃), good biocompatibility, suitable for equipment with high sterilization requirements (such as surgical instruments) | All materials must comply with biocompatibility certifications such as ISO 10993 to ensure non toxicity or sensitization risks when in contact with the human body |
| Aluminum: Lightweight and cost-effective, suitable for weight sensitive medical devices | Polyethylene (PE): Good flexibility, low temperature resistance, suitable for wire harness scenarios that require frequent bending | Polyurethane (PU): Wear resistant, tear resistant, suitable for long-term use of medical consumables such as electrode wires and sensor harnesses | |
| Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE): a combination of rubber elasticity and plastic processability, used for wiring harnesses with high flexibility requirements |
四、Example of Material Application
- High frequency electric knife harness: It adopts PVC outer insulation and internal three core copper wire to meet the high-precision signal transmission requirements.
- Life support equipment wiring harness: Priority should be given to using silicone or PU materials to meet high temperature sterilization and long-term reliability requirements.
Different material combinations can meet the diverse needs of medical equipment, and comprehensive selection is required based on specific scenarios such as power, signal type, and sterilization conditions.
五、Application scenarios
- Widely used in monitors, medical imaging equipment (such as ultrasound equipment), surgical instruments, testing instruments, etc.
- In high-end equipment such as surgical robots and life support systems, higher precision customization requirements need to be met.