By quanyu lee
2024-12-13 07:49:59
Robotic Flexible Cable Harness Guide: How to Choose, How to Test, and How to Extend Service Life
In industrial robots, high-speed sorting machines, collaborative robots, and automated production lines, the lifespan of wire harnesses often determines the stability of the entire system. Ordinary wire harnesses will rapidly age or even break under prolonged bending, cable chain reciprocating, torsion, and acceleration impacts. In contrast, robotic flexible cable harnesses are specifically designed for these high-intensity working conditions, maintaining structural stability and signal integrity even after millions of cycles.
Suppose you are looking for a wiring harness solution for robotic arms, slides, articulated axes, or high-speed dynamic systems. In that case, this guide will help you fully understand the key aspects of bend-resistant robot wiring harnesses, including materials and structure, as well as selection methods.
I. What is a Robotic Flexible Cable Harness?
A flexible robot cable harness is an electrical interconnect designed for highly dynamic motion environments. It usually includes conductors, cables, insulation layers, shielding, buffer materials, connectors, and additional mechanical reinforcement. Compared with standard harnesses, it offers:
1. High Flex Life
Designed to withstand millions—sometimes tens of millions—of bending cycles, such as U-shaped drag-chain loops.
2. Torsion Resistance
Capable of handling repeated twisting motions, often ±180° per meter or more—crucial for rotating robot joints.
3. Tensile & Impact Reinforcement
Kevlar fibers, layered buffering, or mechanical strain-relief structures help prevent conductor breakage under pulling or acceleration.
4. EMI/EMC Shielding
Robotic environments contain strong electromagnetic interference from servo drives and inverters. Stable shielding is essential for reliable signals.
5. Long-Life Jacket Materials
These include PUR, TPE, and high-performance PVC, optimized for oil resistance, wear resistance, and high flexibility.
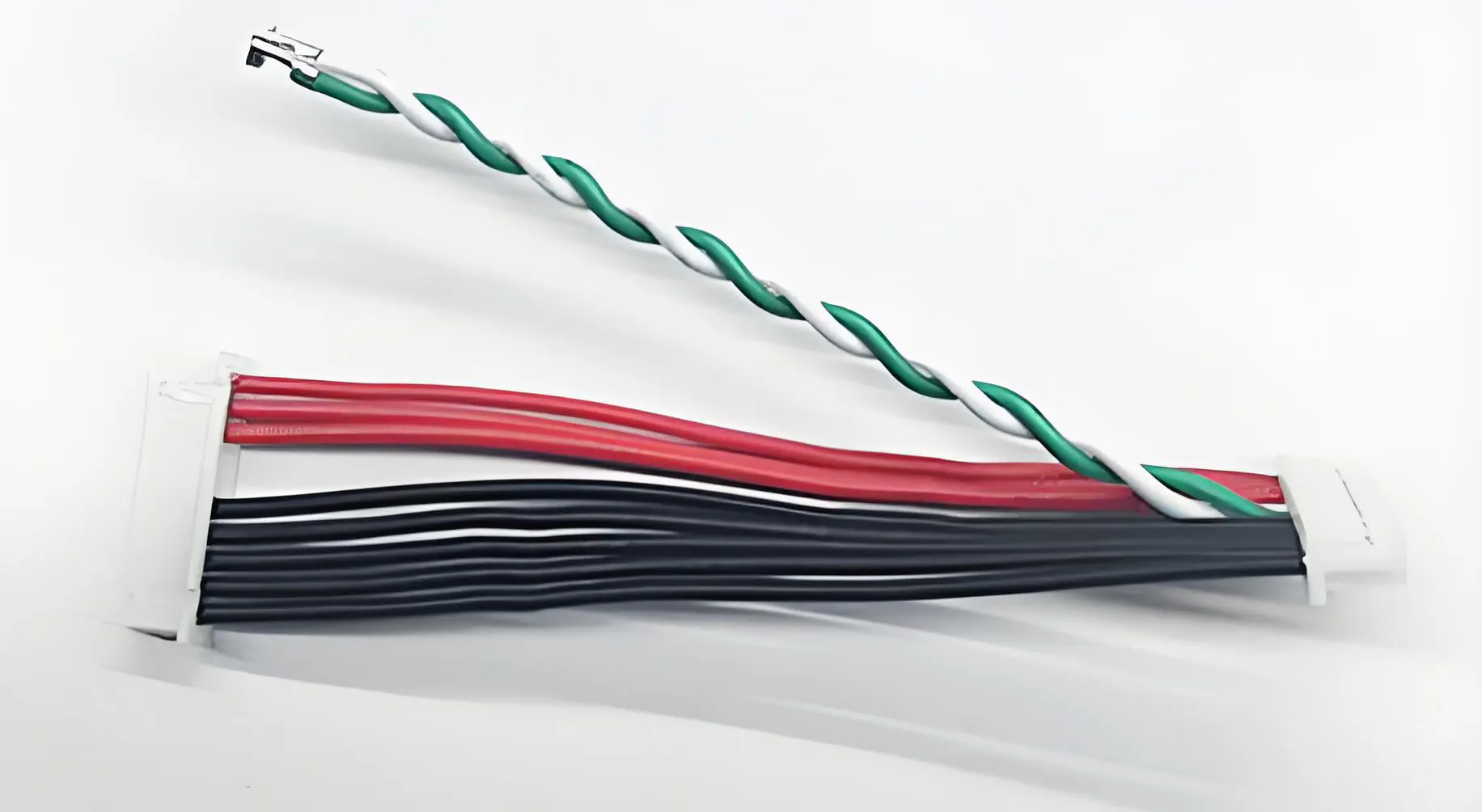

2. Core Structural Elements of a Flexible Robot Cable Harness
To ensure durability and stability, robot-grade harnesses use specialized internal structures:
1. Extra-Fine Stranded Conductors
The thinner the strands, the more flexible the conductor.
- Typical diameter: 0.05–0.1 mm
- Benefit: significantly increased lifespan and bendability
2. Multi-Layer Buffering System
Between the conductor and jacket, buffers such as:
- flexible fillers
- PET braided layers
- low-friction tapes
These help reduce internal friction and prevent stress concentration.
3. Shielding Options
Depending on the application:
- tinned copper braid
- aluminum-foil + braid composite
- 360° continuous shielding
Essential for encoder cables, bus communication lines, and sensitive signals.
4. Jacket Materials
Different materials match different environments:
| Material | Features | Applications |
| PUR | Highly flexible, oil-resistant, wear-resistant | Industrial robot drag chains |
| TPE | Low-temperature resistance, eco-friendly, soft | Cobots |
| High-grade PVC | Cost-effective, medium flexibility | Standard automation |
3. How to Choose the Right Flexible Robot Cable Harness
Selecting a robot cable is more than checking whether it’s “soft.” It must match the real operating conditions.
1. Identify the Motion Type
Different movements impose different stresses:
| Motion Type | Key Requirements | Example Equipment |
| Drag-chain bending | High flex life, low-friction jacket | Robot to control the cabinet |
| Twisting motion | Torsion endurance + tensile strength | Cobots, 6-axis robots |
| 3D compound motion | Hybrid flexibility + special stranding | SCARA, Delta robots |
2. Confirm Electrical Requirements
Robot harnesses often integrate:
- Power cables
- Encoder cables
- Communication buses (EtherCAT, CAN, RS-485)
- Servo motor cables
- I/O signal lines
Key checks:
- Impedance consistency
- Shielding continuity
- A layout that isolates sensitive signals
3. Environmental Conditions
Consider:
- Temperature range (e.g., −40°C to +80°C)
- Exposure to cutting oil or industrial lubricants
- Mechanical shocks or vibrations
- Cleanroom requirements
4. Connector & Termination Quality
Typical robot harness terminations include:
- M12 / M23 circular connectors
- servo encoder interfaces
- custom molded connectors
- anti-strain terminal designs
Most failures occur near connectors, so termination quality is critical.
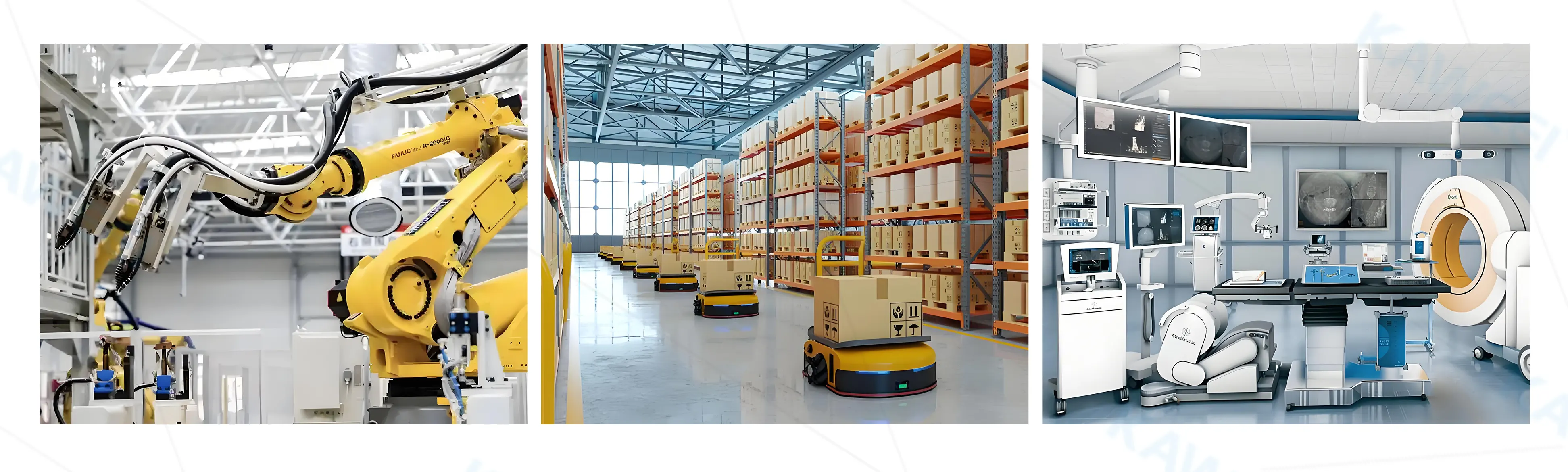

4. Common Application Scenarios
Flexible robot harnesses are widely used in:
- 6-axis industrial robots (welding, handling, palletizing)
- collaborative robots
- high-speed sorting machinery
- laser cutting and spraying systems
- 3D printing and precision automation
- medical automation platforms
- semiconductor equipment
Any scenario requiring continuous motion, micro-positioning, or high-frequency dynamic tasks must use dedicated robotic cable harnesses.
5. How to Tell If a Cable Harness Is Truly “Flexible”?
Standard industry tests include:
1. Bending Life Test
- U-shaped bending with load and speed.
- Validated by 1,000,000+ cycles.
2. Torsion Test
- Repeated twisting such as ±180° or ±360°
- Tests stress distribution in rotating joints.
3. Drag-Chain Durability Test
- High-speed, long-distance, high-frequency motion.
4. Environmental Tests
- salt-spray
- oil-resistance
- temperature shock
- abrasion resistance
Always request from suppliers:
- lifetime curve
- dynamic test parameters
- materials datasheet (datasheet)

6. Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Mistake 1: Using regular control cables instead of robot-grade cables
Result: signal failure or conductor breakage within weeks.
Mistake 2: No motion-length reserve
Creates severe stress on connectors.
Mistake 3: Ignoring electromagnetic interference
Causes encoder noise, servo jitter, and communication loss.
Mistake 4: Incorrect jacket material selection
PVC, for example, degrades quickly in oily environments.
Mistake 5: Improper clamping or fixing
Wrong routing or tying can “choke” a cable during movement.

7. FAQ: Common Questions About Flexible Robot Cable Harnesses
1. How long does a flexible robot cable harness last?
Depending on structure and materials, lifespan ranges from 1,000,000 to more than 20,000,000 cycles.
If you need durable custom harnesses for high-motion robots, WIRE HARNESS ASSEMBLY can design reinforced solutions optimized for your specific bending radius, torsion angle, and motion path.
2. Is torsional life more important than bending life?
Yes—especially for 6-axis robots, torsion resistance is often the primary factor.
3. Can drag-chain cables replace robot cables?
No. Drag-chain cables are not built for multi-axis twisting or compound motion.
4. Do robot cable harnesses require customization?
Most applications require custom solutions because lengths, routing paths, and connectors vary across equipment.
5. How can I extend real-world cable life?
- proper routing
- flexible clamps and strain relief
- avoiding bending below the minimum radius
- high-quality connectors and molding
8. Conclusion
A flexible robot cable harness is not just a "soft cable" but a highly engineered component designed for demanding dynamic environments, which should provide long bending life, strong torsion resistance, stable shielding, optimized material formulation and robust termination craftsmanship, and choosing the right one can significantly improve reliability, reduce downtime and extend the overall system lifespan whether building a high-speed production system or optimizing cable routing for a collaborative robot.



